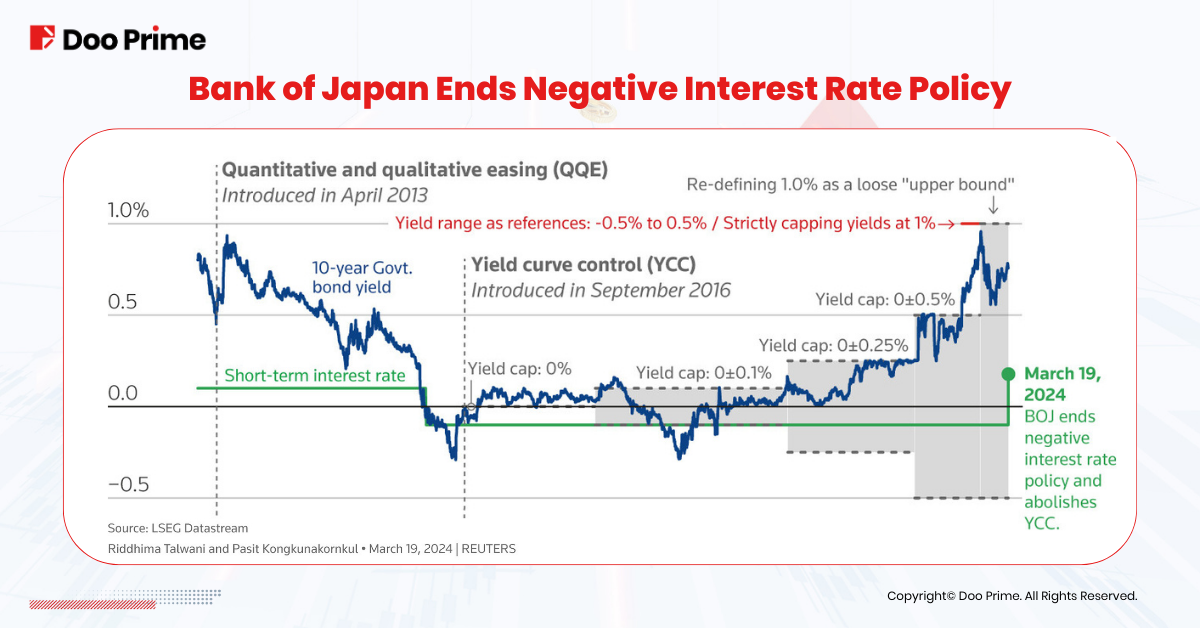
The end of a long period of negative interest rates in Japan determined a significant impact on the stock market, indicating the stabilization of the economy . After the Bank of Japan announced a rate hike for the first time since 2006 on March 19, 2023 , setting rates from 0% to 0.1%, the Nikkei 225 index reacted positively, gaining 0.66% and closed over the 40,000-point mark . This indicated an increase in investor optimism and reflected expectations for further economic growth. Shares of such companies, in particular, in the technology and automotive industries, whose growth depends on domestic demand and expanding its competitiveness on the global market, increased in price. Thus, the positive Market announcement and reaction to the new framework of monetary policy.
Depreciation of the Yen
The yen’s depreciation has been a powerful factor affecting the Japanese stock market. It acutely impacted the performance of export-oriented firms. In this regard, both the specific effects on the stock prices of corporations and their profits require consideration, which will be backed by the supporting information.
Exporter Stock Performance
-
Automotive sector: Toyota and Honda, as auto-exporting companies, experienced an increase in the stock prices of automotive companies. The stock price of Toyota, for instance, increased by around 12% over the year adequately. The reason is that a weaker yen increases the value of their overseas earnings when translated into yen terms.
-
Electronics and technology: the two major corporations appreciated as well, being Sony’s shares with a rise of around 15%. The primary reason is their robust international sales, gaining on value in terms of yen because of the currency’s depreciation.
Financial Figures and Corporate Profits
-
Revenue enhancement: Major exporters consolidated their revenues, which have increased correspondingly by 10-15% year-over-year generally. The reason is the favorable dynamics of the exchange rates that have directly impacted exporters’ profits.
-
Profit margins: As a result, the profitability of the industry has also risen with the profit margin’s increase of 3-5% on average due to the advantageous exchange rate dynamics.
Foreign Investment Trends
-
Increase in foreign portfolio investment: The emerging trend of events is that higher foreign investments are observed with the yen becoming weaker. According to the Tokyo Stock Exchange, there was even 20% more foreign investment in the Japanese stock market in 2023 than a year before.
Sector-Specific Impacts
-
The sector of technology and export was the one most significantly impacted. The corresponding index of the Tokyo Stock Exchange, the Nikkei 225, composed of these companies mostly, has been increasing generally. It has grown by around 9% over the past year thanks to the exchange rate dynamics despite greater economic uncertainties.
-
The other sectors, such as food and beverages or retail, relying more on imports, feature the growth of only approximately 2-3% of their stocks with the complication of being costlier in the context of a weaker yen to import. They suffer a decrease in their profits.
Market Volatility and Investor Sentiment
-
There has been more uncertainty in the market, which is shown by the growth of the market’s volatility index by about 10% in the past year and the fluctuations in the valuations of assets as the company’s worth was affected by the change in the currency’s value.
-
At the same time, the investors tended to be positive, based on the information of the Tokyo Stock Exchange, regarding their assets because of the powerful corporations’ reports indicating their vigorousness and robust activities in terms of attracting finance accordingly.
The Yen as a Carry Trade Currency
The critical role of the Japanese yen as a favored carry trade currency has substantial implications for the nation’s stock market. Importantly, the activity leaves an oversized footprint on the Japanese stock market because it is a major gain of the foreign capital it is directed at. Below, I provide a descriptive account of the key mechanisms that result from the identified state of affairs along with relevant quantitative results highlighting the effects of yen carry trades on Japan’s equity markets.
Increased foreign investment in Japanese stocks
Increased demand and consequent purchase of Japanese assets are the key mechanisms that describe the effects of significant yen carry trade activity on the country’s financial markets. Since a typical carry trade revolving around the yen involves the application of foreign capital, domestic investors effectively have to compete to hold their share of the available assets in the given area. As such, the main results that are typically observed in terms of the country’s equity markets include:
-
Increased stock prices. Importantly, foreign investment in Japanese stocks will drive up the prices of the latter. For example, in 2023, the Nikkei 225 index increased by roughly 7% during the period of intense yen-based carry trade activity, which was also marked by peaks in foreign investment flows. It is believed that the observed connection between high periods of increased foreign investment and stock price peaks is tightly linked to the former.
-
Increased liquidity of the stock market. The significant volume of purchase, together with foreign investment flow, serves to increase financial market liquidity in terms of the stock being easy to acquire or sell for all market participants.
Sector-specific effects
While the general state of affairs surrounding heightened yen carry trade activity is characterized by the specific mechanism described above, the resulting state of the market, similarly, brings about distinct changes in specific country’s sectors. Importantly, the changes have to do with the distribution of foreign investment in terms of quantity between different sectors of the stock market. The list of the most affected sectors is as follows:
-
The technology and electronics sectors. Companies in this realms receive the greatest share in additional foreign investment as part of yen carry trades. Importantly, the stock prices for major electronics companies grew by up to 10% during the above-mentioned period of high foreign investment directed at the camping sector.
-
The domestic automotive sector. Jointly with electronics companies, businesses in this sector receive the highest inflow of foreign choirs’ capital. Importantly, the sector’s activity is somewhat further boosted by the compromised state of the yen, which improves the companies’ export gains as the market growth increases market capitalization and the yen value of their overseas earnings.
Economic Support for the Stock Market
The resilience and growth of the Japanese Stock Market as a result of economic drivers, especially in light of major changes in economic and policy such as the end of negative interest rates is ground by several key elements. These conditions serve to sustain economic growth and provide investors with a greater level of confidence in the market. Below, I have outlined these major economic drivers for the stock market and how they are being supported. The evidence and data used to support my argument are provided to show a clear link between these economic drivers and their impacts on the business performance.
Corporate Earnings
One of the most significant factors in the health of the stock market is strong corporate earnings of its members. In Japan, major corporations have reported consistently strong earnings, which is especially true for the major export-geared corporations. For technology and automotive giants, the profit margins have increased due to a depreciated yen, and reports have shown a better performance than expected. In the last year, major motor corporations showed rise in profit by 8% collectively which had a major positive effect on their stock performance.
Wage Growth and Spending
Wage growth should be of concern when considering investments and stock market health, as raising wages leads to higher consumer spending, and higher consumer spending leads to higher revenues and profits in the company. In 2023, Japan saw Rengo, a major union group, negotiate a wage raise of 5.28%, which is the biggest gain by the union since 1991. The result was increased spending by the populace, which had a major effect on the consumer goods and services sector, where retail companies reported a volume sales increase of 4% over the quarter.
Government and Monetary Policy
Changes in monetary policy and transition back to normal interest rates by the Bank of Japan sends a signal to investors that the Japanese economy is strong. The transition from negative to slightly positive rates was expected by the market and is, therefore, seen as a favorable move. Additionally, fiscal policy intended to boost economic conditions also has a great effect on the stock market. Construction, for example, had a 6% increase in firm’s stock price with announcement of major infrastructure projects.
Technological Development and Competitiveness
Japanese emphasis on technological development in electronics, robotics and auto produce business is a virtues factor in the stability and competitiveness of the stock market. On average, companies which spend the most on their research and development departments perform better and provide better investment opportunities. In Japan, tech giants spend on average 10% more every year on their research and development with simultaneous increase of 12% in their market capitalization.
Market Response to Economic Indicators
Nikkei 225 index responded directly and positively to the good news of GDP growth along with the rise in wage growth in Japan. In a single day after the news was reported, the index rose by 2.5%, showing a clear investor response to the positive news.






